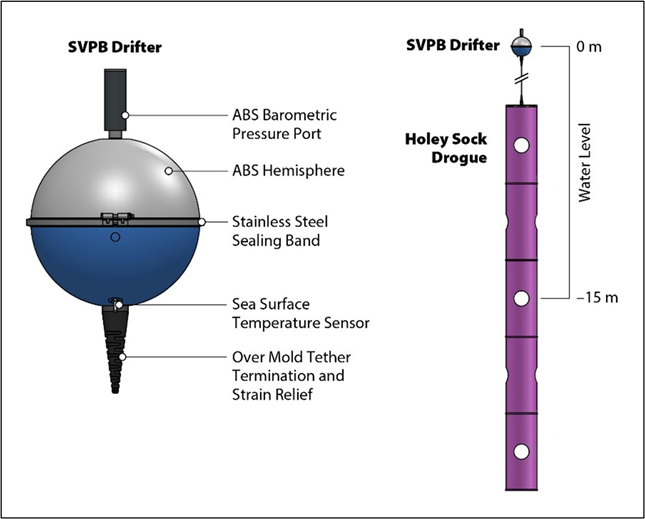
This summer EUMETNET, along with 13 MET Service Providers, have continued to take part in the European Cross Border Convective Advisory procedure for EUROCONTROL’s Network Manager. This year EUMETNET is also deploying operational meteorologists from 6 of these MET ANSPs (Air Navigation Service Providers) to Network Managers Operations Centre, to support their network management activities. The intent is to understand the potential value and additional capability that onsite meteorologists can play in supporting the European Aviation Network.
The Advisories primary goal aims to increase EUROCONTROL’s Network Manager (NM) and participating ATC ANSP’s (Air Traffic Control Air Navigation Service Providers) awareness of potentially significant convection that could disrupt the European Aviation network within the next 12 to 36 hours, to support operational decision makers’ effective and efficient management of the network. However, this year, the cross-border weather procedure is also playing an important role in ensuring that the recovery from COVID-19 is as delay free as possible.
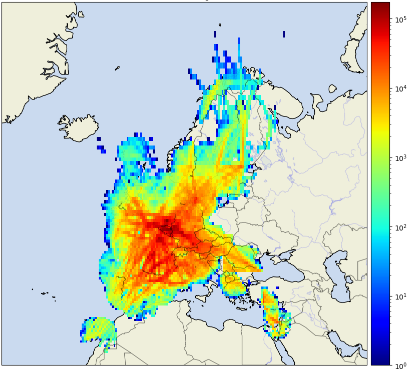
Cumulonimbus (CB) clouds are the main meteorological phenomena that this forecast focuses on, primarily as CB clouds can be used as a proxy for possible ‘weather avoidance’. Weather avoidance is the unplanned movement or deviation from the original flight plan requested at short notice by pilots as a result of ‘weather’ ahead. The reason that pilots would want to avoid these cloud types is due to the hazardous conditions associated within them (e.g. severe turbulence, downdraughts, icing and lightning) and the resultant comfort and safety implication for crew and passengers. Multiple avoidance requests will lead to additional workload and complexity for air traffic controllers, who may then be unable to safely handle the ‘normal’ amount of traffic, and capacity of the airspace is affected, resulting in diversions and delays of flights.
The operational meteorologists, who will be deployed in July and August, will continue to produce the Cross Border Advisory. However they will also liaise directly with the staff at NM to provide a holistic assessment of the weather conditions affecting Europe on a day to day basis and also to learn more about the tasks that NM undertake and where they may have opportunities for additional weather support within their operations.
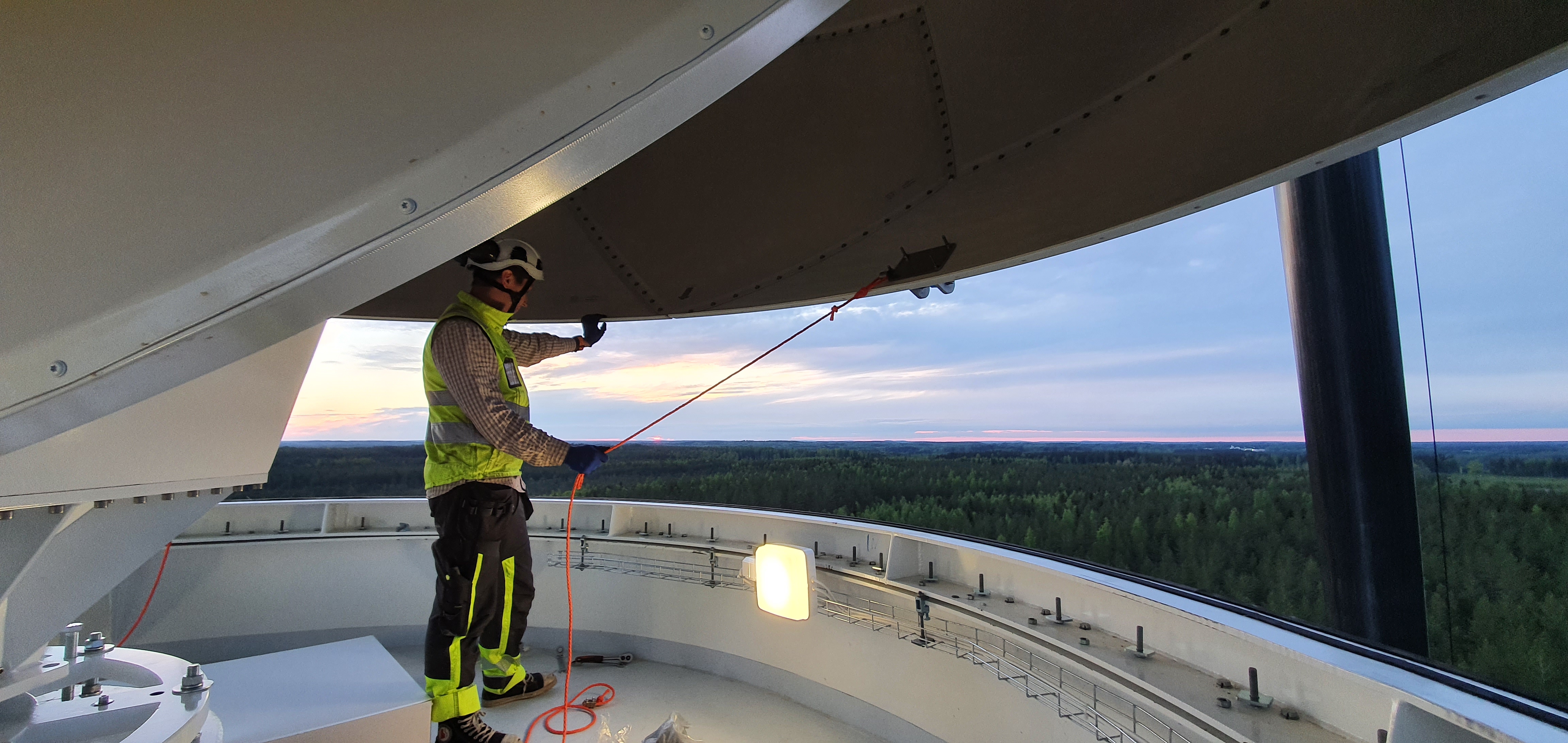
The first meteorologist on site is Pauline Jaunet from Meteo France, she said “It is a pleasure to directly interact with NM operational staff and assist them with better tailored weather forecasts. To promote the use of weather information to better manage the airspace and reduce the risks of disruption is a great opportunity to better understand the impacts the disruptive weather has on the aviation network.”
Iacopo Prissinotti, Director Network Management, EUROCONTROL said “On behalf of the EUROCONTROL Network Manager team I am delighted to welcome MET experts to NM’s operational centre this summer. Mitigating the effects of bad weather on air traffic and ensuring efficient and more sustainable operations is a key priority for us as we strive to deliver the best service to operational stakeholders in Europe. This trial is the latest in a series of NM initiatives in recent years to take a network-minded approach to bad weather with operational stakeholders: with these activities we aim to provide maximum situational awareness for all users when significant adverse weather conditions are identified that could affect multiple sectors.”
Through the relationship that is developing between EUROCONTROL and EUMETNET, the participating MET ANSPs can together help provide advisory forecasts that are consistent within each state but also are effectively communicated to other airspace users regarding the impacts of convective weather so that they can plan for the disruption that may be caused, resulting in fewer delays and happier passengers.